The quantity of carbs present in food with the pace with which it increases your blood glucose levels is called the Glycemic Load. The Glycemic Index is a simple way of choosing a healthy diet. It compares and shows healthy alternatives according to your blood glucose levels. Glucose represents a higher blood glucose level compared to fructose.
Beetroots are packed with essential nutrients, and according to the International GI Tables, it has a GI of 61. It is packed with healthy nutrients and is associated with several health benefits, including improved blood pressure, better blood flow, and increased exercise performance. They are pretty tasty raw but are generally cooked or pickled.

Beetroots come in several types and comprise healthy nutrients like
- Fiber
- Folate
- Manganese
- Potassium
- Iron
- Vitamin C
How to Calculate Glycemic Load of Beetroot?
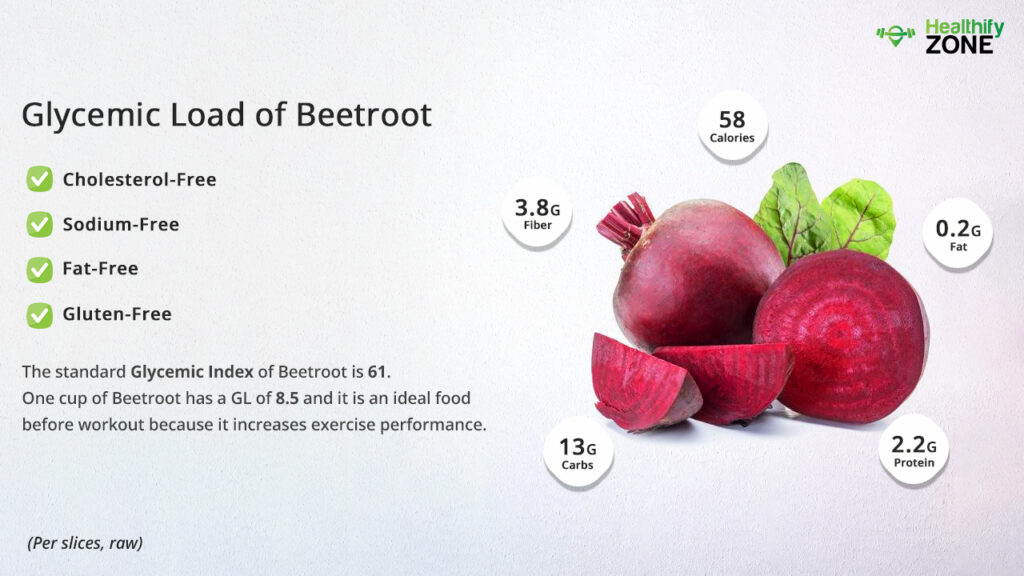
The standard Glycemic index of beetroot is 61. The high glycemic index of the fruit helps in reducing the risks related to cardiovascular diseases. If we want to talk about diet, the key to prevent diabetes or any chronic illness is to distribute the carbohydrate consumption content throughout the day and manage the sugar levels in the body correctly— you can have beetroot as your salad mix and can also have less than a cut of beetroot juice per serving.
The Formula/Procedure For Calculation of Glycemic Index of the Beetroot:
GL = GI * carbs / 100
where
- GL – glycemic load;
- GI – glycemic index;
- and carbs – the amount of carbohydrates in the portion.
| SL.NO | BEETROOT BY WEIGHT IN (g) | GLYCEMIC LOAD |
| 1. | 100 g of Beetroot | 6.1 (low) |
| 2. | 250 g of Beetroot | 15.25 (medium) |
| 3. | 500 g of Beetroot | 30.5 (high) |
| 4. | 1 Cup of Beetroot Juice | 15.3 (medium) |
| 5. | One Whole Beetroot | 7.3 (low) |
| 6. | 1 Cup of Beetroot (140 g) | 8.5 (low) |
Is Beetroot Safe to Consume If You Have Diabetes?
Beetroots are rich in phytochemicals, which have been shown to regulate effect on glucose and insulin levels. Research shows that the antioxidants present in beetroot reduces the risk of diabetes. Metabolites are found in high concentrations in beets, and they are known to reduce insulin resistance. It is necessary that diabetic people consume beetroot in moderation.
Can I Eat Beetroot During a Fat-Loss Diet?
You can eat beetroot during a strict fat-loss diet. If you are looking for good results, you should avoid having more than 200 g of beetroot per serving.

- A 200 g serving of beetroot has a GL of 12.2 which is in the permissible levels.
- Anything more than 150 g of beetroot something which shoud be taken rarely if you are on a fat-loss diet.
Can I Eat Beetroot During a Low-Carbohydrate Diet?
You can eat beetroot during a strict low-carb diet. However, be careful about the portion size you consume. The GL of 100 g of beetroot is 6.1, which means that it does not significantly affect blood sugar levels because of the low carb amount. We suggest you not consume more than 200 g of beetroot per serving.
Is Beetroot High in Sugar?
Beetroot is made of 88% water. 100 g of beetroot has a GL of 6.1, which means that the carb is low. 100 g of beetroot has 10 g carbs and 7 g sugar. It is rather low in sugar compared to other vegetables. You can include beetroot in your diet.